VFD/Inverter Spare Parts
The main hardware of the inverter includes: power devices, busbar capacitors, current sensors, heat dissipation components, drive and control circuit boards, supporting structures, etc. The development of the inverter industry is inseparable from the support of components. This chapter mainly introduces the market status of the above-mentioned main components in the inverter.
1. Power devices
Inverters are generally composed of two parts: rectification and inverter, which are generally separate rectifiers and separate inverter products. Inverters, rectifiers or inverters all work around power devices, so power devices that account for 30% of the cost of inverters are the core and most important components of inverters.
For the rectifier part of the inverter, power devices include diodes, thyristors or IGBTs. Different power devices are selected according to different rectification forms and power segments. Generally, IGBTs are used only for feedback rectification or active rectification. Basic rectification generally uses diodes or thyristors for cost considerations.
The power device of the inverter part of the low-voltage inverter basically uses IGBTs. IGBTs have two structural forms, one is a discrete single-tube type and the other is a multi-tube integrated module type. In the field of domestic inverters, Infineon is in an absolute leading position, with a market share of even 50%.
The good news is that in 2020, STARPOWER Semiconductor, a leading domestic IGBT company, was listed on the main board and was enthusiastically sought after by investors. STARPOWER has entered the top ten in the global market in the field of IGBT modules, and has unlimited development potential. BYD, which is developing rapidly in the field of automotive IGBT, has also broken Infineon's strong position and fully applied it to various self-produced models. I believe that in the near future, domestic IGBTs will rise rapidly and further promote the development of the inverter industry.
1. Bus capacitor

For the inverter, the second largest component besides IGBT is probably the bus capacitor.
The bus capacitor of the inverter generally uses aluminum electrolytic capacitors to smooth the output voltage of the rectifier circuit and provide a stable DC voltage for the inverter behind to reduce the distortion of the AC voltage waveform output by the inverter. In addition, the bus capacitor also plays the role of energy storage and exchange.
Siemens and ABB used to mostly use aluminum electrolytic capacitors from EPCOS of Germany, but in recent years, domestic aluminum electrolytic capacitor manufacturers represented by CECTN have risen rapidly and both have entered the top ten in the world. Not only do domestic inverters use domestic aluminum electrolytic capacitors, but bus electrolytic capacitors are the core components that have made breakthroughs earlier among upstream suppliers of inverters, and are also the only important components of inverters that have entered the procurement catalog of international top inverter manufacturers.
3. Current sensor
The core function of the inverter is to output the appropriate current. Therefore, as a feedback measurement device for current control, the current sensor occupies a very important position in the inverter. The value of the three current sensors matched with each inverter is comparable to that of the bus capacitor.
4. Heat dissipation components
The IGBT, the core component of the inverter, will dissipate heat during operation. Whether the heat of the IGBT can be dissipated in a timely and efficient manner basically determines the life and output capacity of the inverter, and also determines the size and volume of the inverter. Therefore, the heat dissipation components of the inverter are very important. It includes three components: interface material, heat sink and fan/machine.
The interface material is the thermal conductive material filled between the IGBT module and the heat sink. Conventional inverters use thermal conductive silicone grease. Since the thermal conductivity of the base plate (usually copper) and the heat sink (usually aluminum) of the IGBT module are both over 100, the actual contact area on the microscopic contact surface of the IGBT base plate and the heat sink is small, and most of it is separated by air, and the thermal conductivity of air does not exceed 0.05, which is a huge gap. In order to increase the thermal conductivity and transfer the heat of the IGBT to the heat sink as quickly as possible, the interface material is needed to fill the microscopic voids between the base plate of the IGBT module and the heat sink. As shown in the figure below:
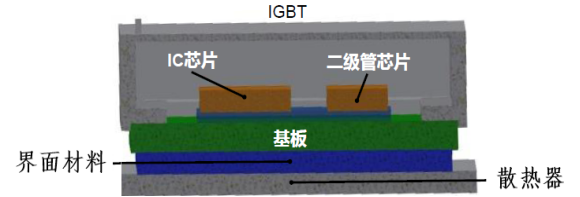
The heat sink of the inverter is basically made of aluminum. In a slightly higher power inverter, only using a heat sink is not enough to dissipate the heat. At this time, a fan needs to be installed. In a higher power inverter, a turbine fan needs to be installed.
5. Drive and control circuit board
The circuit board for controlling and driving around IGBT in the inverter is an important part of the inverter cost. Let's put aside the production of PCB and the processing of PCBA. There are many components on the finished circuit board, including not only conventional resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers, connectors and other conventional electronic devices, but also various chips for control, storage, monitoring and driving. Among them, conventional connectors, including connectors for board connection and IO connection, account for a large proportion of the cost of inverters in the low power range.
6. Supporting structural parts
The structural parts of the inverter mainly include injection molding, sheet metal parts, die castings and copper bars. At present, with the domestic equipment and process level, the structural parts have considerable international competitiveness. The first step in the localization process of imported brand inverters is to localize the structural parts. There are many regional suppliers for various products.
Address: No. 3 Ruzhu Road, Jiangshan City, Zhejiang Province, China
E-mail: info@sowakam.com



